CMSC
0.0050


People with missing teeth may be able to grow new ones, say Japanese dentists testing a pioneering drug they hope will offer an alternative to dentures and implants.
Unlike reptiles and fish, which usually replace their fangs on a regular basis, it is widely accepted that humans and most other mammals only grow two sets of teeth.
But hidden underneath our gums are the dormant buds of a third generation, according to Katsu Takahashi, head of oral surgery at the Medical Research Institute Kitano Hospital in Osaka.
His team launched clinical trials at Kyoto University Hospital in October, administering an experimental medicine to adult test subjects that they say has the potential to jumpstart the growth of these concealed teeth.
It's a technology "completely new" to the world, Takahashi told AFP.
Prosthetic treatments used for teeth lost to decay, disease or injury are often seen as costly and invasive.
So "restoring natural teeth definitely has its advantages", said Takahashi, the project's lead researcher.
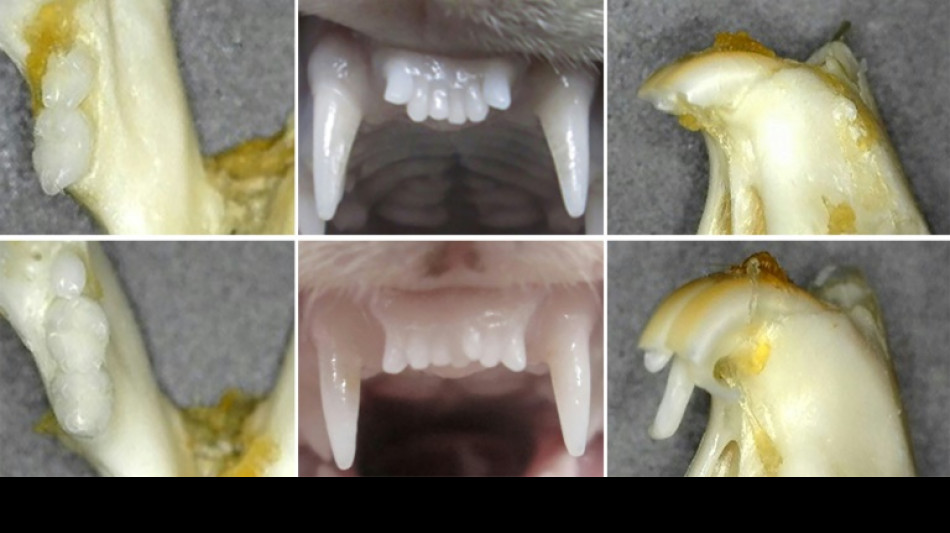
Tests on mice and ferrets suggest that blocking a protein called USAG-1 can awaken the third set, and the researchers have published lab photographs of regrown animal teeth.
In a study published last year, the team said their "antibody treatment in mice is effective for tooth regeneration and can be a breakthrough in treating tooth anomalies in humans".
- 'Only the beginning' -
For now, the dentists are prioritising the "dire" needs of patients with six or more permanent teeth missing from birth.
The hereditary condition is said to affect around 0.1 percent of people, who can have severe trouble chewing, and in Japan often spend most of their adolescence wearing a face mask to hide the wide gaps in their mouth, Takahashi said.
"This drug could be a game-changer for them," he added.
The drug is therefore aimed primarily at children, and the researchers want to make it available as early as 2030.
Angray Kang, a dentistry professor at Queen Mary University of London, only knows of one other team pursuing a similar objective of using antibodies to regrow or repair teeth.
"I would say that the Takahashi group is leading the way," the immunotechnology expert, who is not connected to the Japanese research, told AFP.
Takahashi's work is "exciting and worth pursuing", Kang said, in part because an antibody drug that targets a protein nearly identical to USAG-1 is already being used to treat osteoporosis.
"The race to regenerate human teeth is not a short sprint, but by analogy a set of back-to-back consecutive ultra-marathons," he said.
"This is only the beginning."
Chengfei Zhang, a clinical professor in endodontics at the University of Hong Kong, said Takahashi's method is "innovative and holds potential".
"The assertion that humans possess latent tooth buds capable of producing a third set of teeth is both revolutionary and controversial," he told AFP.
He also cautioned that "outcomes observed in animals do not always directly translate to humans".
The results of the animal experiments raise "questions about whether regenerated teeth could functionally and aesthetically replace missing teeth", Zhang added.
- 'Over the moon' -
A confident Takahashi argues that the location of a new tooth in a mouth can be controlled, if not pinpointed, by the drug injection site.
And if it grows in the wrong place, it can be moved through orthodontics or transplantation, he said.
No young patients with the congenital disorder are taking part in the first clinical trial, as the main objective is to test the drug's safety, rather than its effectiveness.
So for now, the participants are healthy adults who have lost at least one existing tooth.
And while tooth regeneration is not the express goal of the trial this time around, there is a slim chance that it could happen to subjects anyway, Takahashi said.
If so, the researchers will have confirmed that the drug can be effective for those with acquired toothlessness -- which would be a medical triumph.
"I would be over the moon if that happens," Takahashi said.
This could be particularly welcome news in Japan, which has the second-oldest population in the world.
Health ministry data shows more than 90 percent of people aged 75 or older in Japan have at least one tooth missing.
"Expectations are high that our technology can directly extend their healthy life expectancy," Takahashi said.
X.Silva--TFWP