SCS
0.0200


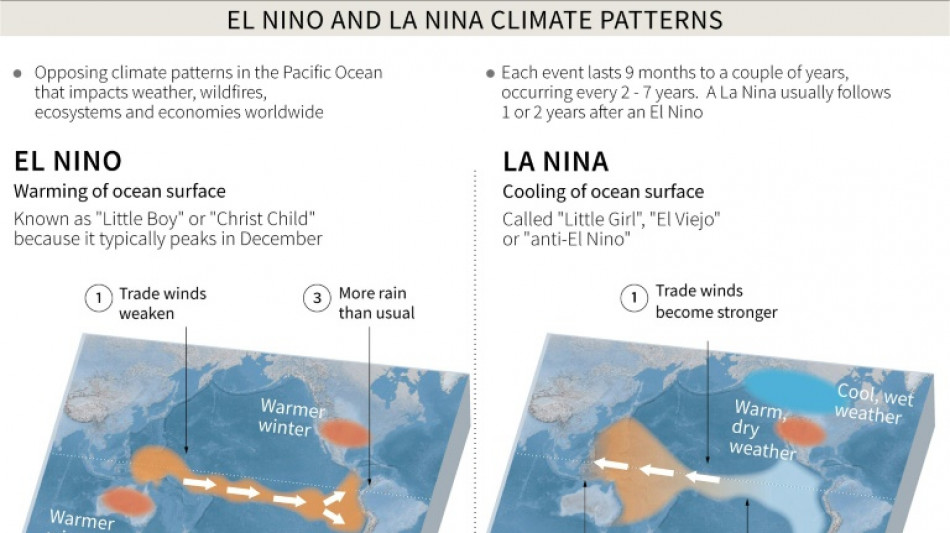
The El Nino weather phenomenon is just warming up, according to scientists, potentially paving the way for higher temperatures and extreme weather events in a year that has already seen plenty of both.
The first El Nino in years began last month, according to the World Meteorological Organization.
The naturally occurring warming of temperatures in the Pacific Ocean typically lasts between nine to 12 months, and is expected become stronger towards the end of the year.
Scientists have warned the impacts of El Nino -- combined with human-induced global warming -- will likely stretch beyond the weather.
- Disease -
Vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue, have been shown to expand their range as temperatures rise.
Scientists warned that El Nino, coming in addition to already dire global warming, could make the situation worse.
"We can see from previous El Ninos that we get increases and outbreaks of a wide range of vector-borne and other infectious diseases around the tropics, in the area that we know is most affected by El Nino," Madeleine Thomson, head of climate impacts at the Wellcome Trust charity, told journalists on Thursday.
The rise stems from two effects of El Nino: unusual rainfall that increases breeding sites for transmitters such as mosquitoes, and higher temperatures that speed up transmission rates of various infectious diseases.
An El Nino in 1998 was linked to a major malaria epidemic in the Kenyan Highlands.
– Health -
It is difficult to calculate exactly how much El Nino contributes to extreme weather events such as wildfires.
But heatwaves themselves pose a significant danger to health.
"It's sometimes named the silent killer because you don't necessarily see it as a threat," said Gregory Wellenius, head of a climate and health centre at Boston University.
"But heatwaves in fact kill more people than any other type of severe weather events."
More than 61,000 people are estimated to have died due to the heat in Europe alone last summer -- when there was no El Nino.
And July 2023 has now been confirmed as the hottest month in recorded history.
- Food security -
"In an El Nino year, there are countries where the chances of having a bad harvest increase, for example in South and Southeast Asia," said Walter Baethgen of the International Research Institute for Climate and Society.
Last month India, the largest rice exporter in the world, restricted its exports due to crop damage from irregular monsoon rains.
According to the researchers, such actions have the potential for dire consequences for countries dependent on the exports, such as Syria and Indonesia, that could face a "triple challenge" during El Nino.
"The rice harvest in those countries may be lower than normal, the rice trade may be more difficult or less accessible in the international market and because of that, the price of rice will be high," said Baethgen.
"This combination of factors pretty rapidly affects the food insecurity problems," he added.
- Economic growth -
The Panama Canal is central to global trade routes, but last week the passageway announced that low rainfall -- which meteorologists said was exacerbated by El Nino -- forced operators to restrict traffic, resulting in an expected $200 million drop in earnings.
The sidelined ships are just one example of how El Nino can hurt the global economy.
A study published in the journal Science in May estimated that past El Ninos cost the global economy more than $4 trillion in the years that followed them.
Impacts from both El Nino and global warming were "projected to cause $84 trillion in 21st-century economic losses", it said.
However researchers at Oxford Economics have argued against these projections, calling El Nino a "new risk, but not a gamechanger".
The costs may remain unclear, but the scientists hope the predictability of El Nino will improve preparedness for the challenges ahead posed by a warming world.
"Preparation is much more effective than emergency responses," Wellenius said.
C.Dean--TFWP