RBGPF
-3.4900


An international team of astronomers on Thursday unveiled the first image of a supermassive black hole at the centre of our own Milky Way galaxy -- a cosmic body known as Sagittarius A*.
The image -- produced by a global team of scientists known as the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration -- is the first, direct visual confirmation of the presence of this invisible object, and comes three years after the very first image of a black hole from a distant galaxy.
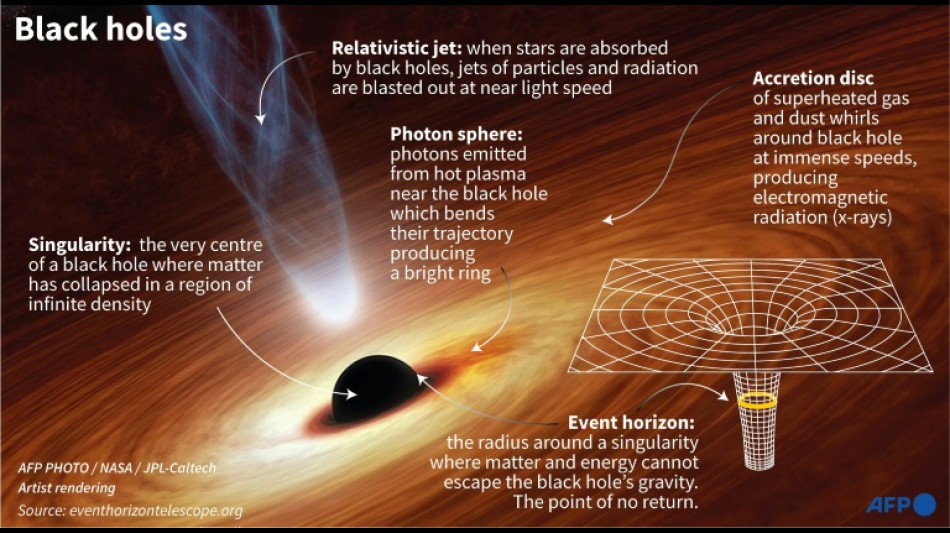
Black holes are regions of space where the pull of gravity is so intense that nothing can escape, including light.
The image thus depicts not the black hole itself, because it is completely dark, but the glowing gas that encircles the phenomenon -- which is four million times more massive than our Sun -- in a bright ring of bending light.
"These unprecedented observations have greatly improved our understanding of what happens at the very centre of our galaxy," said EHT project scientist Geoffrey Bower, of Taiwan's Academia Sinica.
Bower also said in a statement provided by the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) that the observations had offered "new insights on how these giant black holes interact with their surroundings".
The results are published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
- Virtual telescope -
Sagittarius A* -- abbreviated to Sgr A*, which is pronounced "sadge-ay-star" -- owes its name to its detection in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius.
Its existence has been assumed since 1974, with the detection of an unusual radio source at the centre of the galaxy.
In the 1990s, astronomers mapped the orbits of the brightest stars near the centre of the Milky Way, confirming the presence of a supermassive compact object there -- work that led to the 2020 Nobel Prize in Physics.
Though the presence of a black hole was thought to be the only plausible explanation, the new image provides the first direct visual proof.
Because it is 27,000 light years from Earth, it appears the same size in the sky as a donut on the Moon.
Capturing images of such a faraway object required linking eight giant radio observatories across the planet to form a single "Earth-sized" virtual telescope called the EHT.
These included the Institute for Millimetre Radio Astronomy (IRAM) 30-meter telescope in Spain, the most sensitive single antenna in the EHT network.
The EHT gazed at Sgr A* across multiple nights for many hours in a row -- a similar idea to long-exposure photography and the same process used to produce the first image of a black hole, released in 2019.
That black hole is called M87* because it is in the Messier 87 galaxy.
- Moving target -
The two black holes bear striking similarities, despite the fact that Sgr A* is 2,000 times smaller than M87*.
"Close to the edge of these black holes, they look amazingly similar," said Sera Markoff, co-chair of the EHT Science Council, and a professor at the University of Amsterdam.
Both behaved as predicted by Einstein's 1915 theory of General Relativity, which holds that the force of gravity results from the curvature of space and time, and cosmic objects change this geometry.
Despite the fact Sgr A* is much closer to us, imaging it presented unique challenges.
Gas in the vicinity of both black holes moves at the same speed, close to the speed of light. But while it took days and weeks to orbit the larger M87*, it completed rounds of Sgr A* in just minutes.
The researchers had to develop complex new tools to account for the moving targets.
The resulting image -- the work of more than 300 researchers across 80 countries over a period of five years -- is an average of multiple images that revealed the invisible monster lurking at the centre of the galaxy.
Scientists are now eager to compare the two black holes to test theories about how gasses behave around them -- a poorly understood phenomenon thought to play a role in the formation of new stars and galaxies.
Probing black holes -- in particular their infinitely small and dense centers known as singularities, where Einstein's equations break down -- could help physicists deepen their understanding of gravity and develop a more advanced theory.
J.P.Cortez--TFWP