RBGPF
-2.1000


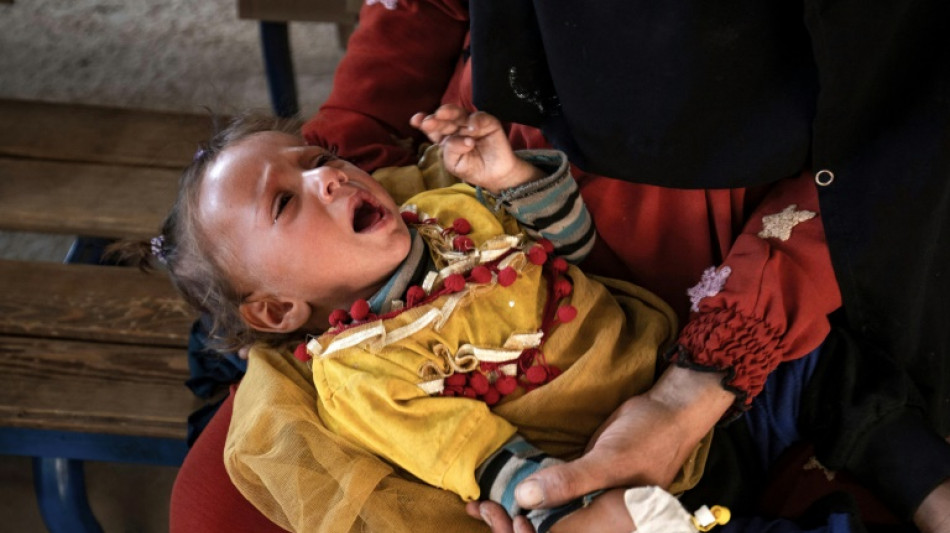
In a Syria hospital crowded with women and wailing children, Ahmad al-Mohammad writhed in pain beside his wife after they contracted cholera, which is resurging for the first time in years.
During his six days in treatment, Mohammad has watched patients stream into the Al-Kasrah hospital in the eastern province of Deir Ezzor, where the highly-polluted Euphrates River is a major source of contaminated water used for both drinking and irrigation.
"We have suffered from diarrhoea, vomiting and pain... because we drink directly from the Euphrates River," the 45-year-old told AFP from the hospital, barely able to speak.
"The waters of the Euphrates are polluted but we have no other choice."
Cholera is generally contracted from contaminated food or water and spreads in residential areas that lack proper sewerage networks or mains drinking water.
The disease is making its first major comeback since 2009 in Syria, where nearly two-thirds of water treatment plants, half of pumping stations and one-third of water towers have been damaged by more than a decade of war, according to the United Nations.
The Syrian government has announced 23 deaths and more than 250 cholera cases across six of the country's 14 provinces since the start of the outbreak in September, with most cases concentrated in the northern province of Aleppo.
The semi-autonomous Kurdish administration that runs northeast Syria and parts of Deir Ezzor has recorded 16 deaths and 78 cases in areas under its control, including 43 cases in western Deir Ezzor, health official Juan Mustafa told reporters Wednesday.
He said water testing of the Euphrates proved the presence of bacteria responsible for cholera -- a spread he said was caused by reduced water flow.
- River pollution -
Said to have once flowed through the biblical Garden of Eden, the Euphrates runs for almost 2,800 kilometres (1,700 miles) across Turkey, Syria and Iraq.
In times of rain, it has offered abundant supplies, gushing into northern Syria through the Turkish border and flowing diagonally across the war-torn country towards Iraq.
But drought and rising temperatures linked to climate change have severely diminished water levels, with the Euphrates experiencing historic lows.
Syria's Kurds have also accused Turkey of holding back more water than necessary in its dams.
The reduced water flow has compounded the problem of river pollution, largely from sewage, but also from oil in hydrocarbon-rich regions, including Deir Ezzor.
Despite the contamination, over five million of Syria's about 18 million people rely on the Euphrates for their drinking water, according to the UN.
The cost of this reliance was visible in Al-Kasrah hospital, where a man softly cradled his infant, an intravenous tube piercing the child's tiny hand.
Hospital director Tarek Alaeddine said the facility admits dozens of suspected cholera cases every day and has tallied hundreds of cases over the past three weeks.
"The patients were all drinking water delivered by trucks that extract it directly from the Euphrates River, without filtering or sterilisation," Alaeddine said.
"We appeal to all international organisations working on health and the environment to act quickly and urgently," he said.
- 'We must live' -
The Britain-based war monitor Syrian Observatory for Human Rights said early this month that the disease had spread in western parts of Deir Ezzor after local authorities stopped distributing chlorine to water pumping stations.
The Kurdish administration, which controls parts of Deir Ezzor including Al-Kasrah, said they have resumed distribution following the outbreak.
They also announced assistance to Al-Kasrah and other medical facilities in the region to help contain the number of cases.
But the main source of the problem remains largely unresolved.
Farmer Ahmad Suleiman al-Rashid, 55, said he irrigated his fields of cotton, okra, spinach and sesame using water from the Euphrates, which caused contamination of crops.
"There are no water filtering stations... we drink unsterilised and unchlorinated water and rely on God for protection," he said
"What else can we do? The authorities are to blame."
As he spoke, a rusty truck pumped water from the murky, green Euphrates.
Meanwhile, irrigation pipelines sucked water out of the river, leaking what appeared to be oil onto the land.
"We know the water is polluted... but we drink it anyway," Rashid said. "We have no other option."
Nearby, a young boy splashed river water on his face to cool down in the summer heat while Sobha Hamid Ali, 60, sat in the shade cleaning spinach leaves.
She too is aware of the dangers but said there is little she can do.
"We are forced to eat contaminated vegetables," Ali said in a soft voice. "We must live after all."
S.Weaver--TFWP