SCS
0.0200


South Asia's annual monsoon rains sustain more than a billion people, but climate change is making them increasingly erratic and deadly, with poor infrastructure only exacerbating the impact.
Farming, water supplies and hydropower across much of South Asia rely on the seasonal rains, but research shows climate change is causing longer dry spells punctuated by bursts of extreme rain.
- What is the monsoon? -
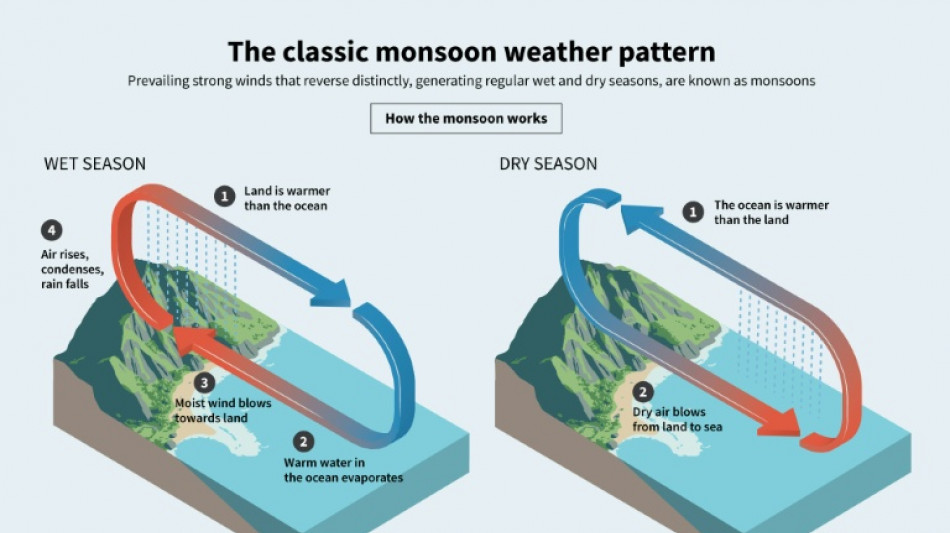
Derived from the Arabic "mausim", or season, the monsoon is a reversal of winds driven by differences in land and sea heating. These patterns are observed in several places on Earth.
In South Asia, the Southwest Monsoon brings rains that start in southern India in late May and sweep north until September.
By October, the Northeast Monsoon begins. As the land cools, winds blow seaward, picking up moisture from the Bay of Bengal before raining over southern India and Sri Lanka.
- What changes are happening? -
"Climate change is beginning to reshape the behaviour of the Indian monsoon", India's government said this year, warning of "more frequent" long, dry stretches and "more intense" wet spells.
Extreme daily rainfall events rose about 75 percent between 1950 and 2015, according to the India Meteorological Department.
Nearly half the season's rain now falls within "just 20 to 30 hours," a government briefing note said.
In Pakistan, the monsoon arrived earlier than usual this year, and "excessive" rain fell in the last week of June, meteorological office spokesman Irfan Virk told AFP.
By mid-August, the country had received 50 percent more rain than last year, according to disaster authorities.
- What role does climate change play? -
The full impact of climate change on monsoon patterns is not entirely clear because of the complexities involved in the seasonal rains.
But "there is a tendency and expectation for more intense and perhaps prolonged monsoons," said Agus Santoso at University of New South Wales' Climate Change Research Centre.
Warmer seas evaporate more moisture into the air, and a warmer atmosphere can hold more moisture, he explained.
"So when it rains, it pours."
But there are other considerations, including the impact of El Nino and La Nina weather patterns, which are themselves more variable, "likely due to climate change," added Santoso.
And predicting future changes is complicated, said climate scientist Shakil Romshoo of the Islamic University of Science and Technology.
"In most of the Indian subcontinent and mountainous regions in the world, we don't have a very dense network of observation," he told AFP.
This makes it "difficult to discern patterns and predict."
- What is the impact? -
The monsoon has long brought floods and landslides to South Asia, but the annual toll has risen over the last decade, experts in India said.
This year, heavy rains also devastated India's breadbasket Punjab region, where rain surged nearly two-thirds above average.
Erratic rains impact soil health and irrigation timing.
"A delay or failure in this season can affect food supply, livelihoods, and the wider economy", India's government says.
In Pakistan, over 1,000 people have been killed in this year's monsoon, nearly triple the figure last year, and rains have prompted massive evacuations in the country's Punjab region.
Standing water can carry disease or encourage reproduction of vectors like mosquitos. Flood damage and evacuations also threaten livelihoods and education across the region.
- What else contributes? -
"Accelerated glacier melt" and deforestation weaken rain-soaked slopes and raise the risk of deadly landslides, according to the Nepal-based International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development.
And vast highways, tunnels, dams and railways carved into mountains without adequate environmental checks only worsen the problem, experts say.
"Rapid, unplanned development, deforestation, river-channel modifications, and poorly sited infrastructure destabilise slopes and block natural drainage," said Anjal Prakash, climate scientist at India's Bharti Institute of Public Policy.
G.George--TFWP